x86 system programming 8 Exceptions and Interrupts
本系列博客用来记录自己对x86体系结构的学习总结,同时方便大家查阅,节省大家学习的时间。 Exceptions and interrupts force control transfers from the currently-executing program to a systemsoftware service routine that handles the interrupting event. Interrupt vector number as index to the IDT. IDT is used in all processor operation modes.(好奇的是,那么言外之意,service routine难道是没有什么特权需要的吗?)
- EXCEPTIONS. software execution error or other internal errors. debug purpose also could happen in this situation(single step, break point), 被称为同步的,因为他们总是由于那个interrupted instructions导致的.
- SOFTWARE INTERRUPTS. occurs as a result of exectuting interrupt instructions. 这个也是同步的. 比较特别的是这个是事先谋划好的(software Interrupts allow intentional triggering of the interrupt-handling mechanism.
- EXTERNAL INTERRUPTS. 这个是asynchronous,they occurs independtly of the interrupted instruction.
masking can refer to either disabling or delaying an interrupt.
8.1 General Characteristics
8.1.1 Precision
1. precise 这个就是说可以保存现场并且回来. 有instruction boundary的概念
2. Imprecise 这个是无法restartable的.
没有完全理解啊。。。 ### 8.1.2 Instruction Restart
1. before the instruction causing the exception.
2. after the instruction causing the exception.
下面这段没有看懂啊。。。头痛
Program state can be updated when the reported boundary is after the instruction causing the exception. This is particularly true when the event occurs as a result of a task switch. In this case, the general registers, segment-selector registers, page-base address register, and LDTR are all updated by the hardware task-switch mechanism. The event handler cannot rely on the state of those registers when it begins execution and must be careful in validating the state of the segmentselector registers before restarting the interrupted task. This is not an issue in long mode, however, because the hardware task-switch mechanism is disabled in long mode. ### 8.1.3 Types of Exceptions
1. Faults rIP -> the faulting instruction
2. Traps rIP -> the instruction following the faulting instruction
3. Aborts imprecise exceptions. do not allow reliable program restart
不要求restart是什么含义?为何就不需要恢复现场了呢? ### 8.1.4 Masking External interrupts
1. Maskable trigger the interrupt-handling mechanism only when RFLAGS.IF=1.
2. Nonmaskable (NMI), however, the occurrence of an NMI masks further NMIs until an IRET instruction is exectuted.
下面看的不是太懂
Masking During Stack Switches. The processor delays recognition of maskable external interrupts and debug exceptions during certain instruction sequences that are often used by software to switch stacks. The typical programming sequence used to switch stacks is:
1. Load a stack selector into the SS register.
2. Load a stack offset into the ESP register.
If an interrupting event occurs after the selector is loaded but before the stack offset is loaded, the interrupted-program stack pointer is invalid during execution of the interrupt handler. To prevent interrupts from causing stack-pointer problems, the processor does not allow external interrupts or debug exceptions to occur until the instruction immediately following the MOV SS or POP SS instruction completes execution. The recommended method of performing this sequence is to use the LSS instruction. LSS loads both SS and ESP, and the instruction inhibits interrupts until both registers are updated successfully. ### 8.1.5 Masking Floating-Point and Media Instructions ### 8.1.6 Disable exception • Alignment-check exception. • Device-not-available exception • Machine-check exception
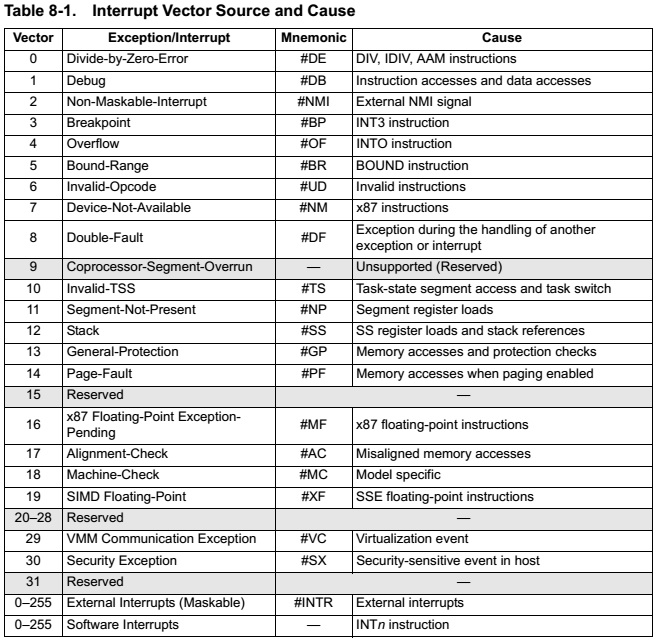
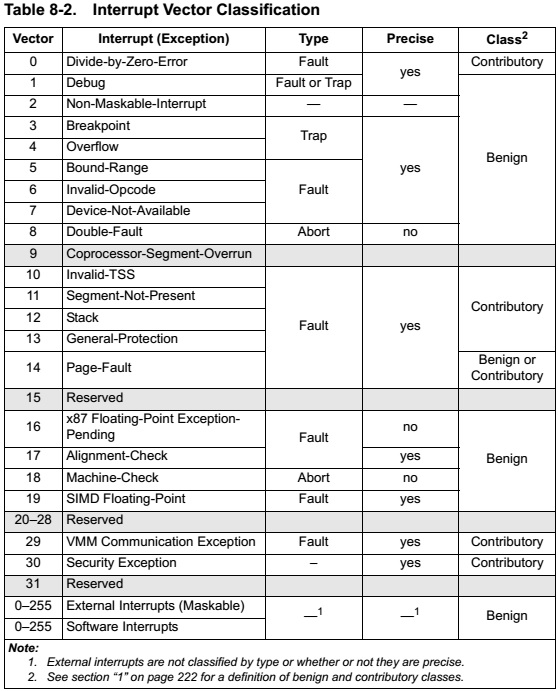
8.2 Vectors
图表和对应的vector类型如下
Written on October 19, 2017
